Morphing
In the context of this book, morphing is the process of interpolation between two geometrical entities. In general, morphing involves two or more initial objects, called parents, and a resulting object (or objects), called child (or children). For the purposes of this example, we will assume two parents and one child. We will also assume that the child’s geometry is the average of the geometry of the two parents. Therefore, if the parents are represented as arrays of points then the child’s array will be created as the average of those points:
for(int i=0; i<child.length; i++)
child[i].x = (parentA[i].x + parentB[i].x)/2;
child[i].y = (parentA[i].y + parentB[i].y)/2;
The above formula would work fine if the parents and child had the same number of points. But that is not necessarily always the case. For example, what if we want to average the points of a 3-point object such as a triangle and a 4-point object such as a square. We would have to find a way to map the two polygons, or in general, a way to map the number 3 to the number 4. Here is what we do (and this is one of the many way to do the mapping): we first create a child object that has the same number of points as the biggest parent, that is, the parent with the most points. So in the above case, the child would have 4 points. Then we map the first three points of the parents one to one and the last extra point of the one parent is mapped to a copy of the last point of the other parent. This is shown in the diagram below:
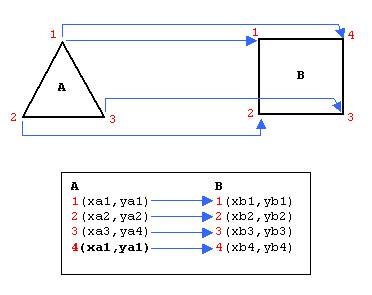
So we map the first 3 and the 4 goes to 1. If we had 3 and 5 we would map the first 3 and the 4 and 5 would go to 1, that is, (1,1), (2,2), (3,3), (1,4), (1,5). And if we had 3 and 6 we would map (1,1), (1,2), (2,3), (2,4), (3,5), and (3,6). These cases, can be generalized in the following algorithm:
for(int k=0; k<Math.max(parentApoints, parentBpoints); k++){
if(parentApoints >= parentBpoints){
fkk = k;
mkk = k/(int) (parentApoints/parentBpoints);
}
else{
fkk = k/(int) (parentApoints/parentBpoints);
mkk = k;
}
child[knt] += (parentA[fkk].x + parentB[mkk].x)/2;
child[knt] += (parentA[fkk].y + parentB[mkk].y)/2;
knt++;
}
We first assume that the child will have the maximum number of point of the two parents. Then we start looping through the child’s points and we take the average of each point from the parent with the least points and selective points from the parent with the most points. The selection is based on the ratio of the counter divided by the number of points of parent A over the number of points of parent B.
import java.awt.*;
import java.applet.*;
import java.awt.image.*;
import java.io.*;
/**
* Morphs two shapes into one,
* and then exits
***********************************/
public class MyMorph
extends Frame {
/**
* Data Members
*************/
long oldTime = -1;
final static long
doubleClickTime = 200;
Point[] p; //the current object
int numpoints; //the current object's points
Point[] parentA;
Point[] parentB;
/**
* The main Frame
constructor and initialization
***********************************/
public MyMorph(){
super("morph");
setSize(800,
600);
p = new
Point[100];
numpoints = 0;
show();
}
/**
* Draw the background
image and the object lines
***********************************/
public void
paint(Graphics g){
for(int
i=0;i<numpoints;i++) {
g.setColor(Color.red);
g.fillOval(p[i].x-2, p[i].y-2,4,4);
if(numpoints>1 &&
i<(numpoints-1))
g.drawLine(p[i].x,p[i].y,p[i+1].x,p[i+1].y);
if(parentA!=null)
for(int j=0; j<parentA.length-1; j++)
g.drawLine(parentA[j].x,parentA[j].y,
parentA[j+1].x,parentA[j+1].y);
if(parentB!=null)
for(int j=0; j<parentB.length-1; j++)
g.drawLine(parentB[j].x,parentB[j].y,
parentB[j+1].x,parentB[j+1].y);
}
}
/**
* Input points and if
double click switch parents
**********************************/
public boolean
mouseDown(Event evt, int x, int y){
//******* If
double-click end polygon
if (oldTime != -1 && Math.abs(evt.when - oldTime) <
doubleClickTime) {
Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().beep(); // beep
if(parentA==null){
parentA =
new Point[numpoints];
for(int
i=0; i<numpoints; i++)
parentA[i] = p[i];
numpoints = 0;
System.out.println("parent
A");
}
else
if(parentB==null){
parentB =
new Point[numpoints];
for(int
i=0; i<numpoints; i++)
parentB[i] = p[i];
numpoints = 0;
System.out.println("parent
B");
morph();
}
}
else
{
Point point = new
Point(x,y);
//Store
point in array
p[numpoints]
= point;
numpoints++;
repaint();
}
oldTime =
evt.when;
return true;
}
/**
* Interpolate the
location of the vertices of the
* two parent objects
***********************************/
public void morph(){
//if(parentA==null
|| parentB==null)return;
int knt = 0;
int fpnts = parentA.length;
int mpnts = parentB.length;
int maxp = Math.max(fpnts, mpnts);
double xChild[];
double yChild[];
int nsteps = 100;
xChild = new double[maxp];
yChild = new double[maxp];
System.out.println("maxp = " +
maxp);
knt = 0;
int fkk = 0;
int mkk = 0;
for(int k=0; k<maxp; k++){
if(fpnts>=mpnts){
fkk = k;
mkk = k/(int)Math.ceil(
(double)fpnts/(double)mpnts); }
else{
fkk = k/(int)Math.ceil(
(double)mpnts/(double)fpnts);
mkk = k; }
xChild[knt] += (parentA[fkk].x +
parentB[mkk].x)/2;
yChild[knt] += (parentA[fkk].y + parentB[mkk].y)/2;
knt++;
}
numpoints = knt;
p = new Point[numpoints];
for(int i=0;
i<numpoints; i++){
p[i] = new Point((int)xChild[i],
(int)yChild[i]);
System.out.println("x = " + (int)xChild[i] + " y= " +
(int)yChild[i]);
}
repaint();
}
//*******
public static void
main(String[] args){
MyMorph mymorph = new MyMorph();
}
}
The result is shown below:
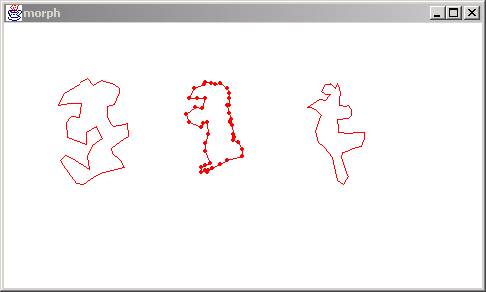
Parent A and B are drawn in the left and right side respectfully and the child object is shown in the middle.